Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to discarded electronic devices and equipment. With rapid technological advancements and increasing consumer demand for the latest gadgets, e-waste has become a significant global issue. Understanding which countries produce the most e-waste and the resulting environmental impact is crucial for developing effective waste management strategies.
Top 5 Electronic Waste Generating Countries
1)China: The E-Waste Leader
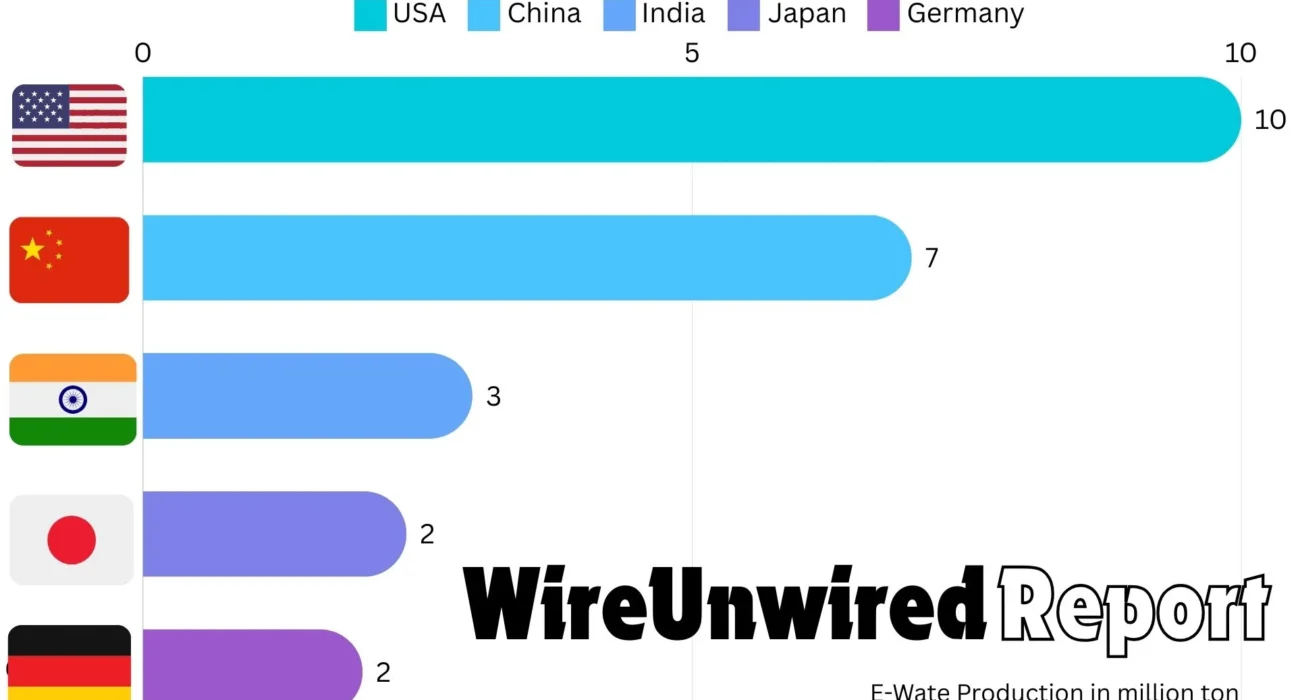
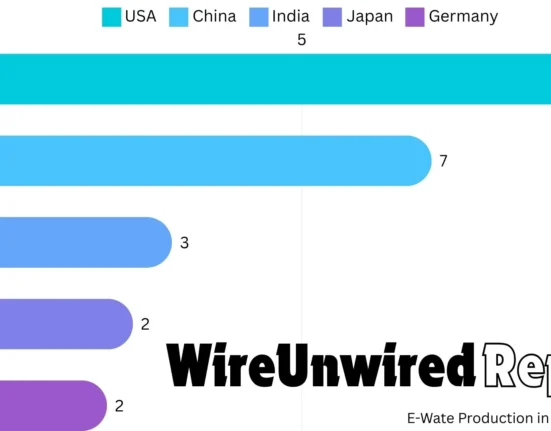
China is the world’s largest producer of electronic waste. In 2023, the country alone generated over 10 million metric tons of e-waste. Several factors contribute to China’s high e-waste levels, including its large population, rapid economic growth, and extensive manufacturing sector.
E-waste has a serious environmental and health impact in China. Improper disposal and recycling processes can release toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium into the environment, contaminating soil and water. These pollutants pose significant health risks to local communities , including respiratory issues, neurological disorders, and developmental problems. China has made efforts to address the issue by implementing stricter regulations on e-waste disposal and promoting recycling initiatives, but more work is needed to effectively manage the growing problem. .
To address this issue, China has implemented various regulations and initiatives. One of the initiatives is ” The National Sword Policy,” which bans the import of foreign waste, aims to reduce the burden on domestic waste management systems. Additionally, efforts to promote formal recycling facilities and increase public awareness are ongoing.
2)United States: The E-Waste Giant
The United States generates approximately 7 million metric tons annually and ranks second in top electronic waste generating countries. High consumption rates of electronic devices and a culture of frequent upgrades contribute to the country’s e-waste problem.
The environmental consequences in the U.S. are substantial, with large amounts of e-waste ending up in landfills. Recycling challenges, such as inadequate infrastructure and low recycling rates, exacerbate the issue. Toxic chemicals from improperly disposed e-waste can leach into the soil and groundwater, posing environmental and health risks.
Various initiatives are underway to combat e-waste in the U.S. These include the Responsible Electronics Recycling Act and state-level e-waste recycling programs. Promoting extended producer responsibility and encouraging consumers to recycle their old electronics are key strategies in mitigating e-waste.
3)India: Rising E-Waste Concerns
India is rapidly becoming a major e-waste producer, generating around 3 million metric tons annually. This much e-waste generation has pushed India at third rank in global electronic waste generating countries. The informal recycling sector, where unregulated and unsafe methods are used to extract valuable materials from e-waste, plays a significant role in the country’s e-waste landscape.
The impact on the environment and public health in India is alarming. Informal recyclers often burn e-waste or use acid baths to recover metals, releasing harmful pollutants into the air and water. These practices pose serious health risks to workers and nearby communities.
The Indian government has introduced several policies to manage e-waste, including the E-Waste Management Rules. These regulations mandate proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste and promote the establishment of formal recycling facilities. However, enforcing these rules remains a challenge.
Also Read: iPhone propels India’s electronics export to $20 Billion.
4)Japan: Advanced Yet Wasteful
Japan, known for its advanced technology industry, produces a significant amount of e-waste, estimated at 2.5 million metric tons per year and thus comes just below India in terms of global electronic waste generating countries. The high rate of technological innovation and consumer preference for the latest devices contribute to Japan’s e-waste generation.
Environmental impact and resource recovery are critical concerns in Japan. While the country has efficient recycling systems, the sheer volume of e-waste makes it challenging to manage effectively. Improperly handled e-waste can lead to soil and water contamination from hazardous materials.
To improve e-waste management, Japan has implemented strict regulations and promotes recycling through the Home Appliance Recycling Law. The government also encourages consumers to return old electronics for proper disposal and recycling.
Join us On LinkedIn
5)Germany: Europe’s E-Waste Hub
Germany is the leading e-waste producer in Europe, generating approximately 2 million metric tons annually. High turnover rates of consumer electronics and appliances drive the country’s e-waste levels.
The environmental implications of e-waste in Germany are significant, with improper disposal contributing to soil and water pollution. However, Germany boasts one of the most efficient recycling systems in the world, with a strong focus on sustainability and resource recovery.
National and EU-level regulations, such as the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, aim to improve e-waste management. These regulations enforce producer responsibility and promote the recycling and reuse of electronic products.
Conclusion
The top five electronic waste-producing countries—China, the United States, India, Japan, and Germany—each face unique challenges and environmental impacts from their e-waste. Addressing this global issue requires coordinated efforts to improve e-waste management, enhance recycling practices, and reduce the production of electronic waste. By understanding and addressing the e-waste problem, we can mitigate its environmental impact and promote a more sustainable future.
E-Waste Related FAQs
1)What is electronic waste? Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to discarded electronic devices and equipment, including smartphones, computers, and household appliances.
2)Why is e-waste a growing concern? E-waste is a growing concern due to the hazardous materials it contains, which can harm the environment and human health if not properly managed.
3)How can individuals help reduce e-waste? Individuals can help reduce e-waste by recycling old electronics, purchasing sustainable products, and supporting companies with responsible e-waste management practices.
Discover more from WireUnwired
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.