In the dynamic and ever-evolving energy landscape, microgrids have emerged as a groundbreaking solution, promising resilience, efficiency, and sustainability. Microgrids, the localized energy systems, offer a multitude of benefits for communities, businesses, and institutions, positioning themselves as a crucial player in the future of energy amidst challenges like climate change, energy security, and grid reliability.
Understanding of Microgrids:
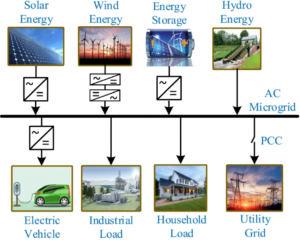
A microgrid is a self-contained, small-scale energy system that integrates various distributed energy resources (DERs) for local electricity generation, storage, and distribution. Unlike traditional centralized power grids, microgrids operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing enhanced flexibility and resilience. These systems draw power from a mix of renewable energy sources—solar panels, wind turbines, biomass—alongside traditional sources like natural gas.
Key Components of Microgrids:
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs): Microgrids leverage a combination of energy resources within or near the community they serve, including renewable sources, energy storage systems, combined heat and power (CHP) units, and backup generators.
- Control Systems: Intelligent control systems form the backbone of microgrids, managing energy generation, distribution, and storage. Utilizing advanced technologies like sensors, automation, and smart algorithms, these systems optimize energy usage, responding dynamically to changes in demand and supply.
- Energy Storage: Microgrids incorporate batteries and other energy storage technologies to store excess energy during low-demand periods and release it during peak times or grid outages, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply.
- Islanding Capability: A defining feature of microgrids is their ability to operate independently in “island mode” during grid outages, enhancing energy resilience. Critical facilities like hospitals, emergency services, and data centers can continue functioning even when the main grid is down.
Advantages of Microgrids:
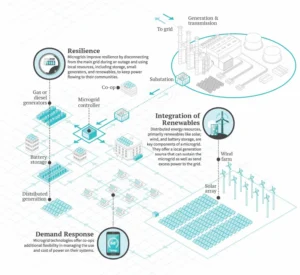
- Resilience and Reliability: Microgrids enhance energy resilience by reducing dependence on a centralized grid. In the face of natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or other disruptions, microgrids continue to supply power to critical facilities, maintaining essential services.
- Energy Independence: Communities and businesses can achieve energy independence by generating power locally, reducing reliance on external sources and gaining greater control over energy costs.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Microgrids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, supporting the transition to a sustainable and low-carbon energy future. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Cost Savings: Microgrids optimize energy usage and reduce transmission losses associated with long-distance power delivery, leading to cost savings for both operators and end-users.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While microgrids offer numerous benefits, addressing challenges such as initial implementation costs, regulatory barriers, and interoperability issues is crucial for widespread adoption. Initial investments can be substantial, deterring potential adopters, and regulatory frameworks need to evolve to accommodate microgrid integration into existing energy infrastructures.
Interoperability and standardization play vital roles in microgrid success, especially when integrating with the main power grid. Seamless communication and coordination between microgrids and the broader energy network are essential for efficient operation and grid stability.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for microgrids is promising. Technological advancements, ongoing research, and increasing awareness of the benefits of decentralized energy systems are driving innovation in the microgrid sector. As costs decrease and regulatory frameworks evolve, the adoption of microgrids is likely to grow, making them an integral part of a resilient and sustainable energy landscape.
conclusion:
Microgrids represent a paradigm shift in energy generation and distribution, paving the way for a more resilient, sustainable, and decentralized future. As communities and industries recognize the value of localized energy systems, the adoption of microgrids is poised to grow, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable global energy landscape. By harnessing the power of distributed energy resources, intelligent control systems, and energy storage technologies, microgrids are not only ensuring reliable energy but also addressing the challenges of climate change, guaranteeing a sustainable energy future for generations to come.
Discover more from WireUnwired Research
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




