Memories have always been critical components contributing to any device’s performance. With increasing heavy memory consuming applications , RAMS role has increased significantly.
Computer memory, also known as RAM (random access/read-write device) and often simply memory, uses random orders to store computer data that a processor needs in applications or between files when accessing them.
In recent times, the new concept of virtual RAM has arisen as a way to expand the available memory on a computer system. But do you know virtual RAMS are slowing down your device’s performance?
In this detailed discussion, we will see the differences between virtual RAM and physical RAM and then try to see how virtual RAM’s are slowing down your device’s performance. By understanding these differences, you can make informed decisions on how to optimize your computer’s memory usage.
Physical RAM vs. Virtual RAM
Physical RAM
Physical RAM, as the name suggests , is the actual hardware in your computer that stores data and instructions that are actively being used by the CPU.
IT serves as the primary memory in computing devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets. Due to its volatile nature , it stores data temporarily and loses all the information once the power supply is removed.
How Physical RAM Works?
Physical RAM provides a high-speed interface for the CPU to access data instantly. When you launch an application, the operating system loads essential data into RAM from the slower storage (like SSD or HDD) to speed up data retrieval. Since RAM has faster read and write capabilities, it allows the CPU to process tasks quickly and efficiently. RAM’s speed is measured in MHz or GHz, indicating the rate at which data can be read and written.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of RAM’s functionality:
Application Request: When an app or process is initiated, the CPU instructs the operating system to load the necessary files into RAM.
Data Storage: The OS transfers essential data from slower storage to RAM, minimizing delay and making data readily available.
Data Accessibility: The CPU can then retrieve data from RAM at high speeds, ensuring smoother and faster execution of commands and processes.
Data Removal: Once the application is closed, the OS clears RAM space, making room for new applications or processes.
Virtual RAM
Virtual memory, or virtual RAM, is a memory management technique that uses part of storage devices like SDD (Solid State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disc Device) when physical RAM is occupied fully.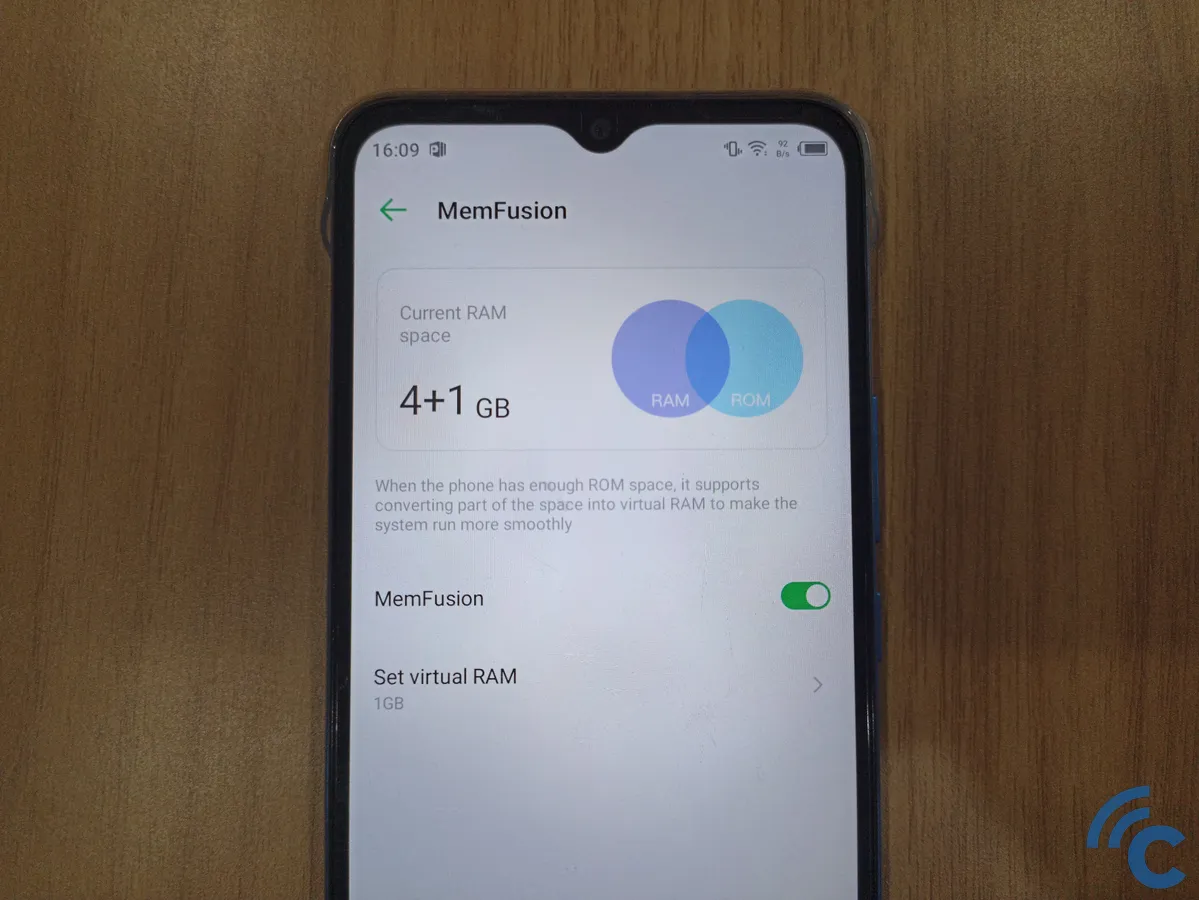
Image source :Carisinyal
This is how the OS can run more apps at a time, storing their memory in RAM while keeping larger datasets on disc by mapping virtual addresses to physical storage.
This is the most important part because when you run out of physical RAM, which could easily happen with only 4GB, your system will start swapping memory off a disc, and everything gets so slow that it can take minutes to get back on track, if not longer.
Storage access speeds are much slower compared to physical RAM, so if a system gets bogged down with the heavy use of virtual memory, then processing slows. However, in the way we use resource management for modern computing systems, virtual RAM cannot be faulted.
Virtual RAMS are slowing down your device’s performance.
As discussed above in virtual ram memory management technique some part of storage devices like SDD (Solid State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disc Device) is used to temporary store files.
So , it will be the SSD’s or HDD’s speed which will determine how our virtual ram is able to transfer temporary files.
So , let’s have a look at what’s the maximum achievable speeds of these storage devices and how does they compare to that of RAM.
1. HDD: 80-160 MB/s, very high latency (~10 ms). This is the slowest one; it bottlenecks significantly when used as virtual memory.
2.SSD: SATA SSDs 500–600 MB/s; NVMe SSDs up to 3,500–7,000 MB/s, with much lower latency (~0.05–0.1 ms). Much faster than HDDs but still far slower than RAM.
3. RAM: It ranges from 15,000 to 25,000 MB/s for DDR4, while DDR5 can reach up to 50,000 MB/s and has extremely low latency, falling in the range of 10–100 nanoseconds.
Clearly we can see that RAM is at least 3-10 times faster than the fastest SSD and 50-150 times faster than HDDs, so relying on HDDs or SSDs as virtual memory can cause performance drops that are easily perceptible.
Apart from the speed issue , virtual RAM affects the device performance in many ways.
1. Inefficient Access Speeds: Storage, even in the case of solid-state drives, is slower than memory. If data accessed the most in a system has to be paged out to virtual memory, the access speed is much lower.
2. More Drive Degradation : Due to heavy paging, SSDs degrade faster than any other form of drive and can start slowing down the storage of their own and eventual paging.
3. Increased CPU Utilization: The CPU has to stay busy with the process of data transfer between RAM and virtual memory, thus degrading power for other applications.
4. Decreased Multitasking Performance: Frequent switching between RAM and virtual memory leads to lag in multi-app scenarios.
5. Slow Response: Applications that use data frequently have a slow response time.
6. HDD Bottleneck: Systems using HDDs for paging experience a high lag due to the lower disk speed.
Should you turn on the virtual ram expansion method on your device ?
In general, it is better to increase physical RAM to maximize performance where possible. This would ensure faster data access and reduce the use of virtual memory, making the operation smoother and more responsive to the system, especially when running applications such as gaming or video editing.
However, increasing physical RAM may not always be necessary, depending on the specific needs and capabilities of the system.
- With 4GB RAM or less: Enable virtual memory if needed, but expect slower performance.
- With 8GB+ RAM: Avoid virtual memory for better speed; rely on physical RAM or consider upgrading.
Conclusion
Virtual RAM essentially complements the system to carry out more tasks in the event of a lack of physical RAM, although corresponding trade-offs affect the system’s performance. Physical RAM is relatively faster and provides the best environment for working applications since they are accessed directly by the CPU. Virtual RAM employs slower storage drives, such as SSD or HDD. It comes with latency, increased CPU workload, and quicker SSD wear. This could cause applications to be less responsive, multitasking less effective, and system lags visible on those that significantly rely on virtual memory.
Discover more from WireUnwired Research
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




