Haptic buttons aim to replace mechanical buttons in smartphones
One of the most common components of smartphones are the mechanical buttons, such as the power button and the volume button. These buttons provide tactile feedback to the user when they are pressed, and they also serve as physical interfaces for various functions of the device. However, mechanical buttons have some drawbacks, such as being prone to wear and tear ,making phone difficult to be water resistant, taking up space, and limiting the design flexibility of the smartphone.
A possible solution to these problems is to replace mechanical buttons with haptic buttons. Haptic buttons are virtual buttons that use haptic technology to create the sensation of touch on a flat surface. Haptic technology is the use of vibrations, forces, or motions to simulate the feel of an object or a gesture. For example, when a user presses a haptic button on a smartphone, they would feel a vibration or a click that mimics the feedback of a mechanical button.
 Haptic buttons replacing mechanical power buttons.
Haptic buttons replacing mechanical power buttons.
Advantages of Haptic buttons over Mechanical Buttons.
Haptic buttons have several advantages over mechanical buttons. First, they can reduce the cost and complexity of manufacturing smartphones, as they eliminate the need for separate components and wiring. Second, they can improve the durability and water resistance of smartphones, as they eliminate the gaps and holes that can allow dust and moisture to enter. Third, they can enhance the user experience and accessibility of smartphones, as they can provide more customizable and adaptive feedback, such as changing the intensity or pattern of the vibration according to the context or preference of the user.
Adoption Problems in Haptic buttons
Haptic buttons are not a new concept, as they have been used in other devices such as gaming controllers, smartwatches, and laptops. However, they have not been widely adopted in smartphones yet, mainly due to technical challenges and user acceptance. Some of the technical challenges include creating realistic and consistent haptic feedback across different surfaces and materials, optimizing the power consumption and battery life of haptic devices, and integrating haptic sensors and actuators into thin and flexible smartphone designs. Some of the user acceptance issues include overcoming the habit and preference for mechanical buttons, adapting to different types of haptic feedback, and trusting the reliability and accuracy of haptic devices

Despite these challenges, haptic buttons are expected to become more prevalent in smartphones in the near future, as haptic technology improves and users become more familiar with it. Some smartphone manufacturers have already introduced haptic buttons in their products, such as Huawei’s Mate 30 Pro, which replaced the volume buttons with haptic ones. Other smartphone manufacturers are also experimenting with haptic buttons for various functions, such as camera shutter, fingerprint scanner, and navigation keys.
Haptic buttons technology is not only used for creating virtual buttons on smartphones, but also for other purposes. For instance, haptic buttons technology can be used to create immersive experiences in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), by providing realistic sensations of touch and movement that match the visual stimuli. Haptic technology can also be used to enhance communication and social interaction, by enabling users to send and receive tactile messages or gestures that convey emotions or intentions. Haptic technology can also be used to improve education and training, by providing feedback that helps learners acquire skills or knowledge more effectively.
Conclusion:
Haptic buttons are an innovative way to replace mechanical buttons in smartphones, as they offer benefits in terms of cost, durability, design flexibility, user experience, and accessibility. However, they also face challenges in terms of technical feasibility and user acceptance. Haptic technology is still evolving and improving, and users are still learning and adapting to it. Therefore, haptic buttons may not completely replace mechanical buttons in smartphones anytime soon, but they may coexist with them or complement them in certain situations.
Hope you liked the article ,do write in comments how u liked the article ,if interested you can also join our WhatsApp community
Until then Keep WireUnwiring like us .
These are Articles.
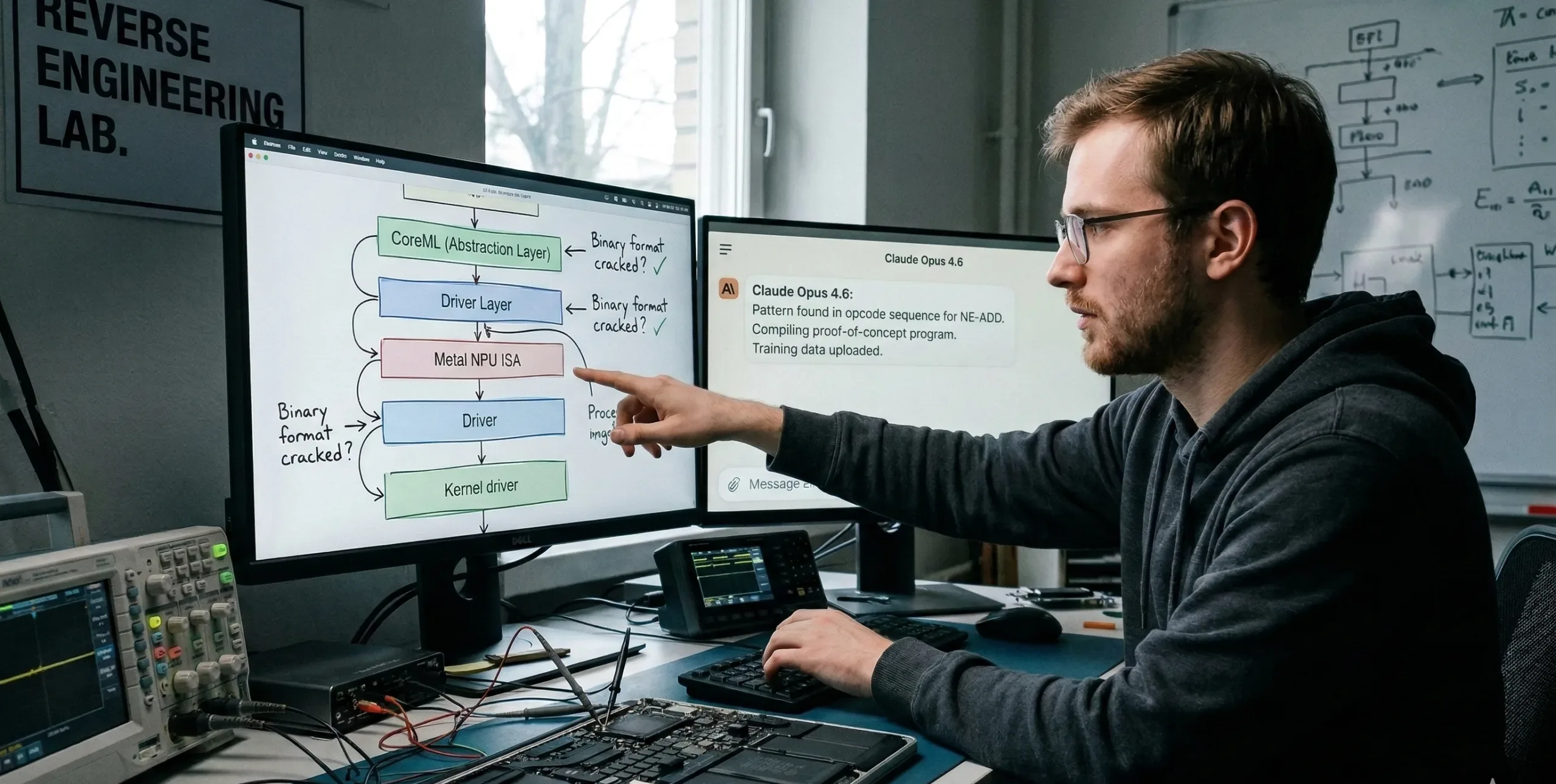
Researchers cracked Apple's Neural Engine, bypassing CoreML. Discovered direct access, trained models on inference-only hardware.
Discover why LLMs like ChatGPT nail complex code and math but produce generic emails and essays. It's not a bug—it's the lack of verifiable feedback. Explore the RLHF gap driving AI's uneven progress
Finance Hits the Same AI Wall as Insurance—85% Want Agents, Only 25% Can Trust Them
85% of finance firms want agentic AI but only 25% have governance—same trust gap as insurance. Sentient launches Arena to test agent explainability.
OpenAI Claims Better Safety Than Anthropic in Military AI Deal—Then Gets Roasted by Users
OpenAI on X annouced deal with Department of War ,claiming 'more guardrails' than Anthropic in DOD deal. Users on X mock this saying I hope your company goes down the toilet.
Discover more from WireUnwired Research
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.