The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked a high-stakes technological arms race between the three centers of AI power – the United States, China, and the European Union. This race for AI dominance could reshape geopolitics and national security over the next few decades.
The State of AI Development Across Major Countries
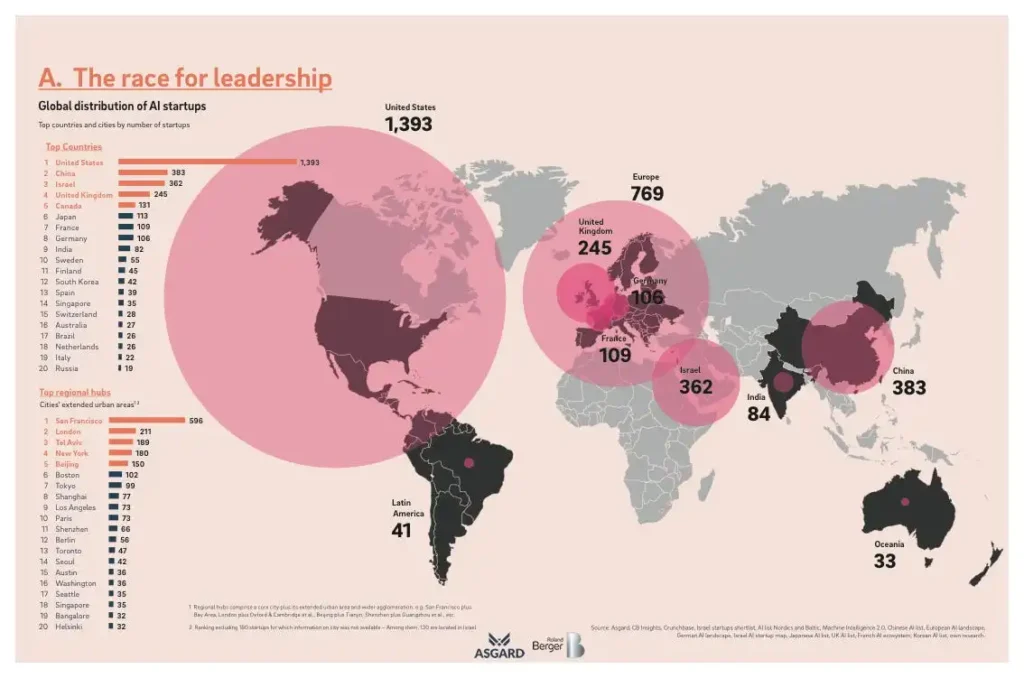
United States Aims to Maintain AI Supremacy
The United States has historically led AI research and still retains that top position, having the world’s largest concentration of AI talent. The U.S. military was an early adopter of AI technology for defense and national security applications. While federal AI legislation remains lacking, some U.S. states have passed laws regulating AI usage across sectors.
The United States has a more reactive, precedent-based approach to artificial intelligence (AI) regulation in the ongoing global AI arms race. While there is currently no comprehensive federal legislation governing AI, individual states have enacted laws imposing limits on the use of AI systems across different industries.
President Joe Biden has released an executive order mandating AI manufacturers to furnish data utilized for training and testing AI models, along with providing performance metrics. The order aims to promote innovation and healthy competition within the country’s AI sector by attracting greater investments and allocating state funding towards public-private partnerships pursuing advancements in artificial intelligence. With China rapidly developing its AI capabilities, analysts observe that the US approach focuses on retaining its lead in the worldwide geopolitical AI race by backing a vibrant AI ecosystem while keeping in view ethical considerations.
China’s Ambition to Lead the AI Race by 2030
Buoyed by strong governmental support and access to vast data, China aims to lead the global AI industry by 2030. Chinese tech giants like Baidu and Alibaba are aggressively developing AI capacities across healthcare, transportation, finance and more.
China has adopted a more centralized approach to governing artificial intelligence (AI) systems as it vies for global dominance in the intensifying AI arms race. The country has established robust regulatory structures to oversee AI development – spanning emerging technologies like generative AI services. China’s strategy for leading the geopolitical AI race fuses accelerated homegrown innovation with strong state supervision and social safeguards attuned to its political economy.
The sweeping 2017 New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan outlines China’s ambition to seize the pole position in AI technology by 2030 amid increasing competition with the United States. With powerful state backing, rapid advances by Chinese tech giants like SenseTime and ecommerce behemoths Alibaba in realms like facial recognition and smart cities have raised concerns over uses violating civil liberties. As China continues its quest to shape technical standards and norms around AI applications with Chinese characteristics, its regulatory model marked by state control over data and algorithms aims to tilt the geopolitical scales in its favor.
EU’s Balanced Approach Focused on Ethics and Regulation

While behind the AI capabilities of the U.S. and China, the EU leads in AI ethics and regulation. The EU’s AI Act aims to ensure harmonized implementation of AI rules across member countries. AI development in the EU focuses on human-centric values and transparency.
The European Union has implemented a broad regulatory framework to govern the development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, a key area of focus in the global AI arms race. The landmark EU AI Act concentrates on enabling harmonized implementation of AI laws across European member states. The legislation mandates transparency, accountability, human oversight and compulsory risk assessments for high-risk AI applications across sectors like healthcare and transport.
Drawing on lessons from the EU’s strong data privacy regime under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the AI Act stipulates that usage of personal data by AI systems must align with existing digital governance laws on processing citizens’ data ethically. As democratic values around human rights shape Europe’s pursuit of trustworthy AI, analysts observe that the emphasis on ethics-by-design in EU’s policies contrasts with AI governance models in the United States and China. With AI poised to become a crucial geostrategic technology of the 21st century, the EU aims to balance rapid innovation with strengthening human agency and control as other leading powers like the US and China angle for dominance in the global AI race.
Key Areas of AI Application and Competition
Defense

Advanced AI abilities like autonomous weapons, drone surveillance systems and decision support architecture are revolutionizing modern warfare. Both China and the U.S. view leadership in military AI as crucial for geopolitical power.
The global artificial intelligence (AI) arms race has accelerated the development of advanced military applications between superpowers – from autonomous weapons to battlefield decision support systems. The United States military has pioneered the use of AI across critical capabilities ranging from surveillance drones to monitoring soldier fitness. In contrast, China has aggressively invested in AI weapons like drone swarms alongside unmanned combat vehicles to gain an edge.
As the geopolitical AI race intensifies, leading militaries are exploring increasingly lethal AI-powered systems like drone fleets that can coordinate to attack targets without human oversight. China has focused intensely on unmanned aerial vehicles and swarming techniques enabled by artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. China’s advances have raised concerns on triggering instability as it develops asymmetric AI capabilities to shift the global balance of power. Simultaneously, as reported by the Government Accountability Office, the US military also experiments with AI drone swarms responding autonomously using distributed data. While the European Union has sought to apply checks through its AI Act, analysts worry that the absence of global norms around military AI could spiral into unstable arms race dynamics between the US and China.
Healthcare

AI is bettering patient outcomes through early diagnosis, personalized treatment and accelerated drug testing. While U.S. hospitals focus on AI for imaging and robotic surgeries, China utilizes AI to provide affordable healthcare for its large aging populace.
China has leveraged AI to speed up drug development and testing processes, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods. The EU has developed digital health passports using AI and blockchain technology to store and share COVID-19 vaccination records and other health-related data. and also developing chatbots and virtual assistants for mental health care, providing support and resources to patients.
Autonomous Vehicles

The self-driving vehicle market is forecasted to expand globally in the coming years. U.S. automakers have an early edge but Chinese and European companies are aggressively playing catch up with bigger investments in AI-powered driverless cars.
In autonomous driving AI is used to develop self-driving cars that rely on sensors, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to navigate roads and avoid obstacles. AI is used to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety on roads. China is investing heavily in autonomous driving technology, with companies like Baidu and Alibaba developing self-driving cars and trucks. In china AI is used to optimize logistics operations, including route planning, vehicle scheduling, and cargo tracking. EU is developing regulations for autonomous vehicles, including the AI Act, which establishes human oversight and transparency requirements for AI systems in vehicles.
Political and Security Implications of the AI Race

Rising tensions between the U.S. and China over leading AI advancement carries global consequences. As these AI superpowers diverge in their regulatory approaches, it could cause worldwide instability. Collaboration in AI ethics and standard-setting is thus increasingly necessary.
Ultimately, balancing competition with cooperation in AI development and governance will be vital for distributing its benefits fairly worldwide while mitigating risks. Global policymaking forums on AI will play a key role in shaping geopolitics in the AI age.
Conclusion
The landscape of AI research and application is evolving rapidly, keyed to economic and national security demands. While the U.S. and China are likely to continue dominating, the dynamics can change based on factors like access to talent, data and computing resources. Ultimately, balancing competition with cooperation is critical for reaping AI’s benefits responsibly and equitably across the world. Careful policymaking and dialogue around AI will shape geopolitical tensions in the coming decades.
Discover more from WireUnwired Research
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




